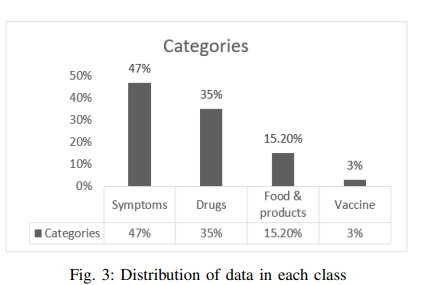
Intelligent Arabic-Based Healthcare Assistant
Text classification has been one of the most common natural language processing (NLP) objectives in recent years. Compared to other languages, this mission with Arabic is relatively restricted and in its early stages, and this combination in the medical application area is rare. This paper builds an Arabic health care assistant, specifically a pediatrician that supports Arabic dialects, especially Egyptian accents. The proposed application is a chatbot based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) models after experimenting with Two Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) models
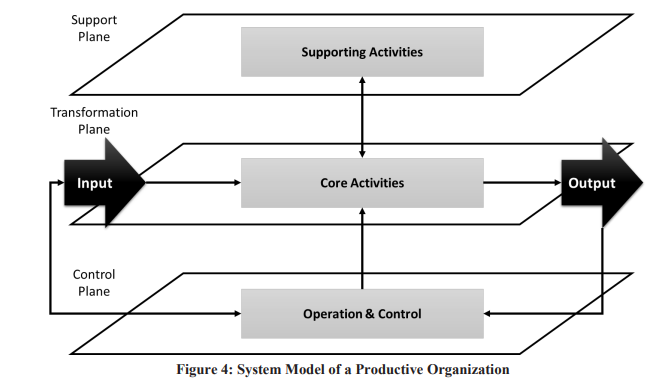
Future of public organizations in the digital transformation era
Introduction and Purpose: Digital transformation has been a “buzz” word over the last few years. Government of Egypt has initiated various ambitious initiatives and projects for transforming the economy into digital economy. Since the outlook of the future organizations would be different from what we know today, therefore, such transformation mandates radical change in the way public leaders manage their organizations, operations and workforce. Consequently, there is a necessity for foreseeing the drivers of change, as well as the technological evolution, which are shaping the future
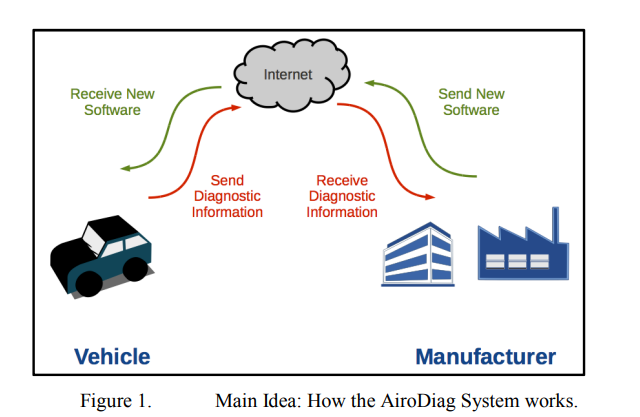
AiroDiag: A sophisticated tool that diagnoses and updates vehicles software over air
This paper introduces a novel method for diagnosing embedded systems and updating embedded software installed on the electronics control units of vehicles through the Internet using client and server units. It also presents the communication protocols between the vehicle and the manufacturer for instant fault diagnosis and software update while ensuring security for both parties. AiroDiag ensures maximum vehicle efficiency for the driver and provides the manufacturer with up-to-date vehicle performance data, allowing enhanced future software deployment and minimum loss in case of vehicle
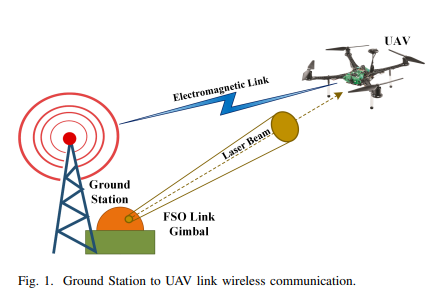
Design and Analysis of A Reliable Quadcopter UAV for Wireless Communication Purposes
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are used for a wide range of applications, including wireless communication systems, which have the potential to provide cost-effective wireless connectivity for a wide variety of applications. The present UAV models lack the flexibility needed to carry the mission's varied payloads. As a result, appropriate design and analysis of the UAV structure are essential. This work presents a complete design and analysis of a quadcopter UAV for wireless communications purposes, which is carried out using computer-aided design (CAD) tools and techniques. Several design
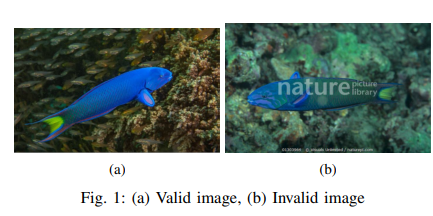
Real-Time Fish Detection Approach on Self-Built Dataset Based on YOLOv3
Creating a model to detect freely moving fish underwater in real-time is a challenging process for two main reasons. First, the available datasets suffer from some limitations that severely affect the results of the detection models operating in challenging and blurry environments. These models should be able to capture all of the fish movement given different types of surroundings. Second, choosing the convenient detection model system which matches the desired requirements from having high accuracy with satisfying frames per second (FPS). To overcome the first challenge, a new dataset was
Hybrid NOMA-based ACO-FBMC/OQAM for next-generation indoor optical wireless communications using LiFi technology
Light fidelity (LiFi) has successfully achieved high data transfer rates, high security, great availability, and low interference. In this paper, we propose a LiFi system consisting of a combination of non-orthogonal multi-access (NOMA), asymmetrically-clipped optical (ACO), and filter bank multicarrier (FBMC) techniques combined with offset quadrature amplitude modulation (OQAM). The paper also applies a μ-law companding approach for a high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) reduction of the FBMC/OQAM scheme. The combination of NOMA, ACO-FBMC/OQAM, and μ-law companding allows a significant
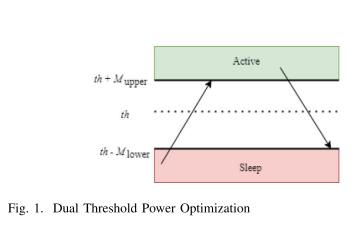
Optimal Power Consumption on Distributed Edge Services Under Non-Uniform Traffic with Dual Threshold Sleep/Active Control
Mobile edge computing (MEC) is a key enabling technology for supporting high-speed and low latency services in the fifth generation (5G) and beyond networks. MEC paradigm moves computational resources from centralized cloud servers towards the edge of the network, nearer to the users. However, edge computation resources increase the power consumption of the network. Moreover, the non-uniform traffic load on the edge servers causes resources to be underutilized and decrease the system's power efficiency. To achieve the green networking concept encouraged in 5G and beyond networks, unused MEC
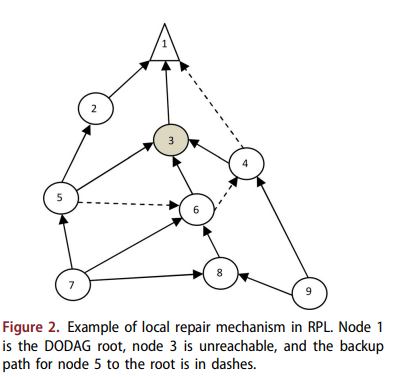
Optimal proactive monitor placement & scheduling for IoT networks
This work is fulfilled in the context of the optimized monitoring of Internet of Things (IoT) networks. IoT networks are faulty; Things are resource-constrained in terms of energy and computational capabilities; they are also connected via lossy links. For IoT systems performing a critical mission, it is crucial to ensure connectivity, availability, and network reliability, which requires proactive network monitoring. The idea is to oversee the network state and functioning of the nodes and links; to ensure the early detection of faults and decrease node-unreachability times. It is imperative
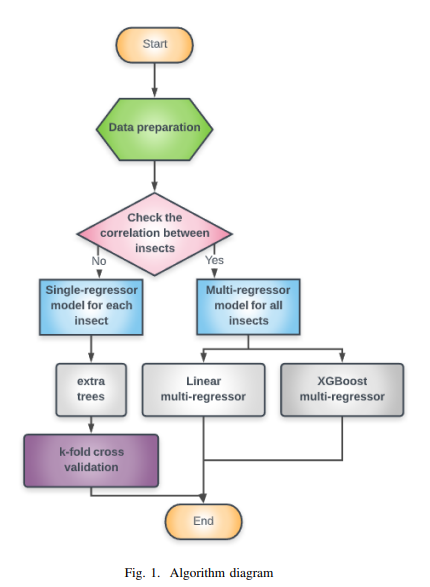
Guava Trees Disease Monitoring Using the Integration of Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
The increase in population, food demand, and the pollution levels of the environment are considered major problems of this era. For these reasons, the traditional ways of farming are no longer suitable for early and accurate detection of biotic stress. Recently, precision agriculture has been extensively used as a potential solution for the aforementioned problems using high resolution optical sensors and data analysis methods that are able to cope with the resolution, size and complexity of the signals from these sensors. In this paper, several methods of machine learning have been utilized
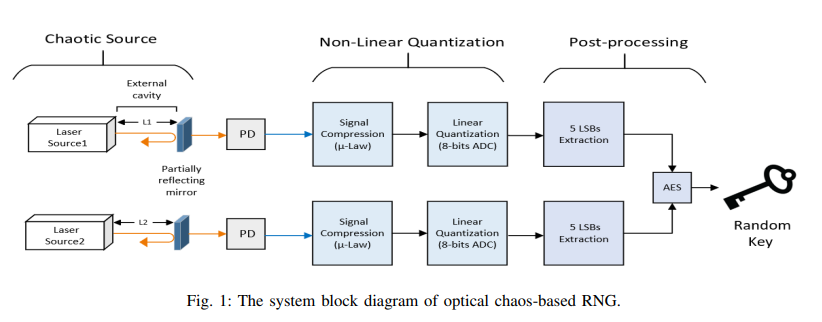
Chaos-Based RNG using Semiconductor Lasers with Parameters Variation Tolerance
Random numbers play an essential role in guaranteeing secrecy in most cryptographic systems. A chaotic optical signal is exploited to achieve high-speed random numbers. It could be generated by using one or more semiconductor lasers with external optical feedback. However, this system faces two major issues, high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) and parameter variations. These issues highly affected the randomness of the generated bitstreams. In this paper, we use a non-linear compression technique to compand the generated signal before it is quantized to avoid the effects of the PAPR. Also
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 57
- Next page ››
