Real-time vehicle detection and tracking using haar-like features and compressive tracking
This paper presents a real-time vision framework that detects and tracks vehicles from stationary camera. It can be used to calculate statistical information such as average traffic speed and flow as well as in surveillance tasks. The framework consists of three main stages. Vehicles are first detected using Haar-like features. In the second phase, an adaptive appearance-based model is built to dynamically keep track of the detected vehicles. This model is also used in the third phase of data association to fuse the detection and tracking results. The use of detection results to update the
Experimental digital forensics of subscriber identification module (SIM) Card
[No abstract available]
Modeling the impacts of information and communication technologies and virtual activities on activity and travel behavior: Case study of Cairo, Egypt
The boom in telecommunications is expected to have many impacts on peoples' activities and travel behavior. Recent advances in information and communication technologies (ICTs) make it possible to conduct activities virtually. Thus the need for physical travel for some types of activities is obviated. Accordingly, the use of ICT may contribute to reducing urban congestion and alleviating air quality problems. However, ICT may generate significant additional travel because of the increased connectivity and access to resources. Empirical insights on how the growing use of ICT affects travel
Comparing maintenance strategies for overlays
In this paper, we present an analytical tool for under-standing the performance of structured overlay networks under churn based on the master-equation approach of physics. We motivate and derive an equation for the average number of hops taken by lookups during churn, for the Chord network. We analyse this equation in detail to understand the behaviour with and without churn. We then use this understanding to predict how lookups will scale for varying peer population as well as varying the sizes of the routing tables. We also consider a change in the maintenance algorithm of the overlay, from
Real-time 2DHoG-2DPCA algorithm for hand gesture recognition
Hand gesture recognition is one of the most challenging topics in computer vision. In this paper, a new hand gesture recognition algorithm presenting a 2D representation of histogram of oriented gradients is proposed, where each bin represents a range of angles dealt with in a separate layer which allows using 2DPCA. This method maintains the spatial relation between pixels which enhances the recognition accuracy. In addition, it can be applied on either hand contour or image representing hand details. Experimental results were performed on the latest existing depth camera dataset. The
Traffic Analysis for Real Time Applications and its Effect on QoS in MANETs
Quality of Service (QoS) is one of the major challenges in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks (MANETs), due to their nature and special characteristics. QoS depends on different and multiple metrics such as routing protocols, route stability, channel rate quality, bandwidth, ... etc. Most of studies focus on the above metrics and some of them proposed enhancements. However, there are still unfilled gaps that need to be tackled. In this paper, we focus on the impact of QoS parameters on MANETs. The main objective is to identify the suitable applications in MANETs with respect to the network parameters. ©
Cooperation incentives in wireless ad hoc networks
Mobile ad hoc networks heavily rely on nodes' cooperation for packet forwarding. As a result, misbehaving, malicious, and selfish nodes can significantly degrade the performance of the network. To cope with this issue and to stimulate cooperation among selfish mobile nodes, a continuous research effort is done on identifying nodes trust and reputation. In this paper, we survey recently proposed reputation and incentive schemes for ad hoc networks. In order to help in the design of different reputation systems tailored to specific applications and network topologies, we classify the different
Reconstruction of High Resolution image from a set of blurred, warped, undersampled, and noisy measured images
This paper proposes an algorithm to reconstruct a High Resolution (HR) image from a set of blurred, warped, undersampled, and noisy measured images. The proposed algorithm uses the affine block-based algorithm in the maximum likelihood (ML) estimator. It is tested using synthetic images, where the reconstructed image can be compared with its original. A number of experiments were performed with the proposed algorithm to evaluate its behavior before and after noise addition and also compared with its behavior after noise removal. The proposed system results show that the enhancement factor is
Arithmetic optimization approach for parameters identification of different PV diode models with FOPI-MPPT
The Maximum Power Point Tracker (MPPT) provides the most efficient use of a Photo-voltaic system independent of irradiance or temperature fluctuations. This paper introduces the modeling and control of a photo-voltaic system operating at MPPT using the arithmetic optimization algorithm (AOA). The single and double Photo-voltaic models are investigated. Their optimal unknown parameters are extracted using AOA based on commercial Photo-voltaic datasheets. A comparison is performed between these optimal parameters extracted by AOA and other optimization techniques presented in the literature
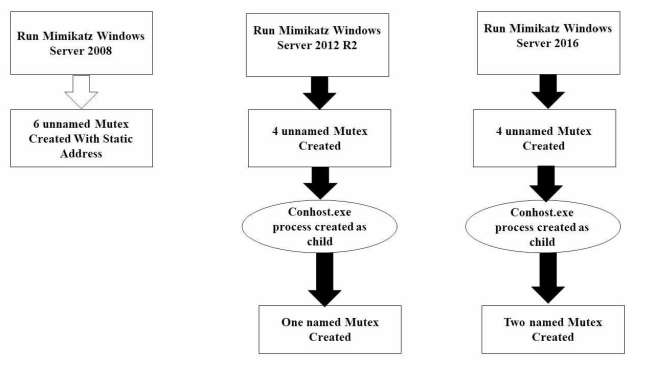
Detecting Mimikatz in Lateral Movements Using Mutex
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is a stealthy computer network attack. Its threat lies in the fact that unauthorized access to a network is gained and the attackers, whether a person or a group may remain undetected for an extended period. APT group can spread and gain access to the most valuable assets in the targeted organization. Depending on the tools used by APT group it can be hard and complex to respond to those groups and their tools. Mimikatz is one of the most powerful tools used by many APT groups, penetration testers and malware. In this paper, we focus on lateral movement and APT
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 55
- Next page ››
