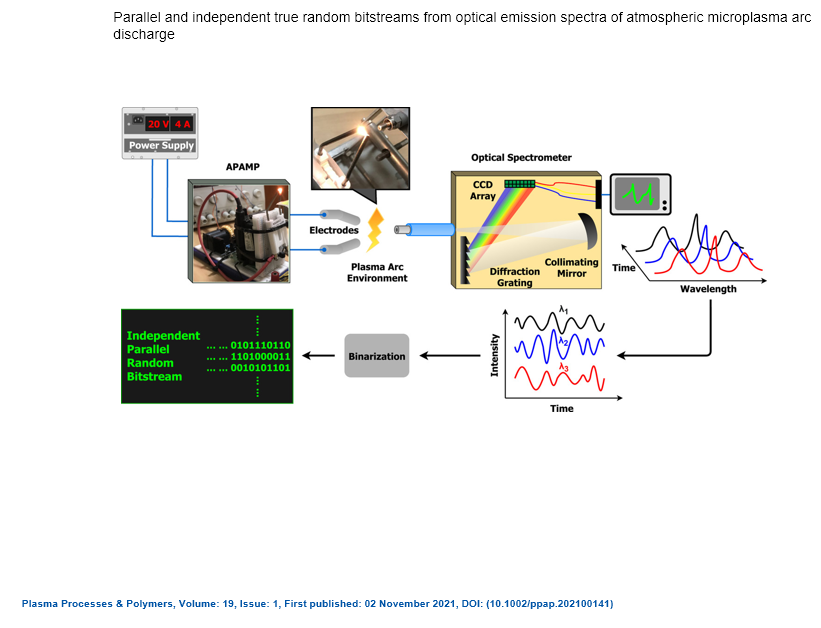
Parallel and independent true random bitstreams from optical emission spectra of atmospheric microplasma arc discharge
In this study, we propose the possibility of generating several parallel and independent random bitstreams from the time-varying optical emission spectra of an atmospheric pressure air microplasma system. This is achieved by splitting the plasma arc emission into discrete wavelengths using an optical spectrometer and then monitoring the fluctuating intensities of each wavelength as an independent time series. As a proof of concept, we considered eight wavelengths centered at 377.8, 389.1, 425.8, 591.4, 630.5, 673.0, 714.2, and 776.4 nm corresponding to atomic emissions lines from species
Anonymous routing protocols in MANETs, a security comparative analysis
A Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) is considered a type of network which is wireless and has no fixed infrastructure composed of a set if nodes in self organized fashion which are randomly, frequently and unpredictably mobile. MANETs can be applied in both military and civil environments ones because of its numerous applications. This is due to their special characteristics and self-configuration capability. This is due to its dynamic nature, lack of fixed infrastructure, and the no need of being centrally managed; a special type of routing protocols such as Anonymous routing protocols are needed
Tunnel-Based EAP Effective Security Attacks WPA2 Enterprise Evaluation and Proposed Amendments
Tunnel-Based Extensible Authentication Protocol has become fundamental for wireless Network access Control. It provides authentication, privacy and authorization for enterprise network access protected by WPA/WPA2 security framework. WPA2 is considered the latest and most secure standard for wireless communication especially for Wi-Fi networks. However, WPA/WPA2-PSK have been lately threatened by advanced versions of wireless attacks. In this paper, we study WPA/WPA2-Enterprise authentication with Tunnel-Based EAP common methods focusing on their strength and weak points and the impact of
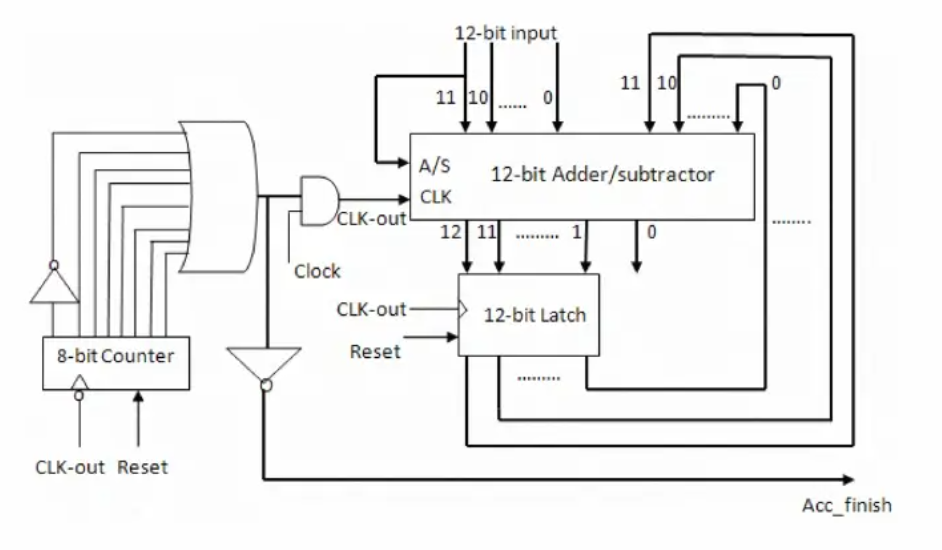
A simplification in integral frequency offset estimation based on joint detection algorithm for WiMAX 802.16e
Initial downlink synchronization for orthogonal frequency division multiple access ( OFDMA ) network access involves timing and frequency synchronization. The frequency offset is produced by oscillator drifts and time-varying Doppler shifts. In mobile WiMAX 802.16e carrier frequency offset (CFO) can be divided into: integral carrier frequency offset (ICFO) and fractional carrier frequency offset (FCFO). There are mainly three methods for CFO estimation: data-aided method, blind and semi-blind. This paper is based on the semi-blind method presented in "Joint detection of integral carrier
Reliability and Security Analysis of an Entanglement-Based QKD Protocol in a Dynamic Ground-to-UAV FSO Communications System
Quantum cryptography is a promising technology that achieves unconditional security, which is essential to a wide range of sensitive applications. In contrast to optical fiber, the free-space optical (FSO) link is efficiently used as a quantum channel without affecting the polarization of transmitted photons. However, the FSO link has several impairments, such as atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors, which affect the performance of the quantum channel. This paper proposes a quantum key distribution (QKD) scheme that uses a time-bin entanglement protocol over the FSO channel that suffers
Hardware Advancements Effects on MANET Development, Application and Research
Mobile devices' development has remarkably improved in light of the fast growing hardware advancements. These advancements include multicore processor chips, ultra large main memories and batteries that last for hours even when running modern applications such as file transfer, voice communication and video streaming ...etc. In this paper, we shed the light on recent and future trends of hardware advancements for mobile devices, and their impact on MANET developments. In addition, the effect of such advancements is investigated on application and different research areas. © Springer-Verlag
Towards mature temporal accuracy assessment of processors models and simulators for real-time systems development
Modeling and simulation are becoming extensively used in embedded and Real-Time Systems (RTSs) development throughout the development life-cycle, from the system-level design space exploration to the fine grained time analysis and evaluation of the system and even its components performance. At the core of these systems lies the processor which has been also the center of attention for most of the modeling and simulation efforts related to RTS simulation. Although the temporal accuracy of such models and simulators is of critical importance for Real-Time (RT) applications, it is not yet mature
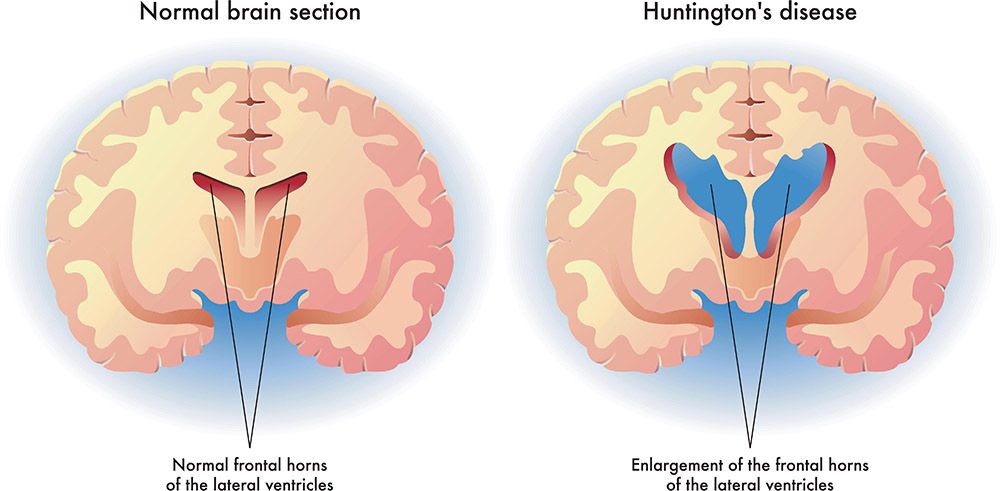
INVESTIGATION OF DIFFERENTIALLY EXPRESSED GENE RELATED TO HUNTINGTON'S DISEASE USING GENETIC ALGORITHM
neurodegenerative diseases have complex pathological mechanisms. Detecting disease-associated genes with typical differentially expressed gene selection approaches are ineffective. Recent studies have shown that wrappers Evolutionary optimization methods perform well in feature selection for high dimensional data, but they are computationally costly. This paper proposes a simple method based on a genetic algorithm engaged with the Empirical Bays T-statistics test to enhance the disease-associated gene selection process. The proposed method is applied to Affymetrix microarray data from
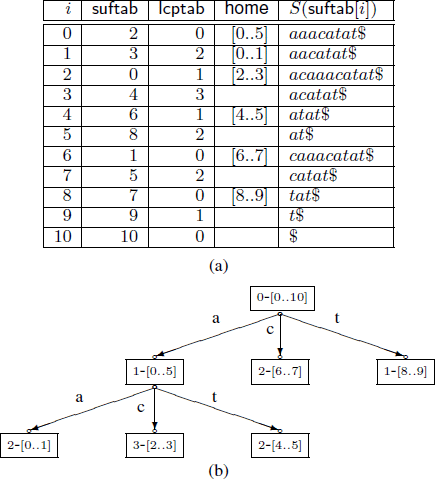
Fine tuning the enhanced suffix array
The enhanced suffix array is an indexing data structure used for a wide range of applications in Bioinformatics. It is basically the suffix array but enhanced with extra tables that provide extra information to improve the performance in theory and in practice. In this paper, we present a number of improvements to the enhanced suffix array: 1) We show how to find a pattern of length m in O(m) time, i.e., independent of the alphabet size. 2) We present an improved representation of the bucket table. 3) We improve the access time of addressing the LCP (longest common prefix) table when one byte
CoCoNUT: An efficient system for the comparison and analysis of genomes
Background: Comparative genomics is the analysis and comparison of genomes from different species. This area of research is driven by the large number of sequenced genomes and heavily relies on efficient algorithms and software to perform pairwise and multiple genome comparisons. Results: Most of the software tools available are tailored for one specific task. In contrast, we have developed a novel system CoCoNUT (Computational Comparative geNomics Utility Toolkit) that allows solving several different tasks in a unified framework: (1) finding regions of high similarity among multiple genomic
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 52
- Next page ››
