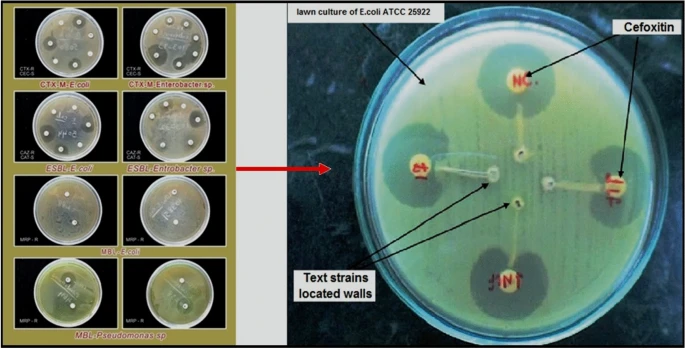
Molecular identification of extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs)-producing strains in clinical specimens from Tiruchirappalli, India
Worldwide, the phenomenal antimicrobial resistance with its consequences of fatal diseases has been alerted; it is because the morbidity and mortality at a shocking rate. Therefore, there is an urgent quest of innovative antimicrobials agents; it is that communicable disease is a worldwide trouble as of the growth and wideness of drug-resistant pathogens. As for the aim of the research, it is widely investigative to the prevalence of Gram-negative pathogens of E. coli and K. pneumoniae in different age groups, gender along with the identification of ESBL-producing pathogens and antimicrobial
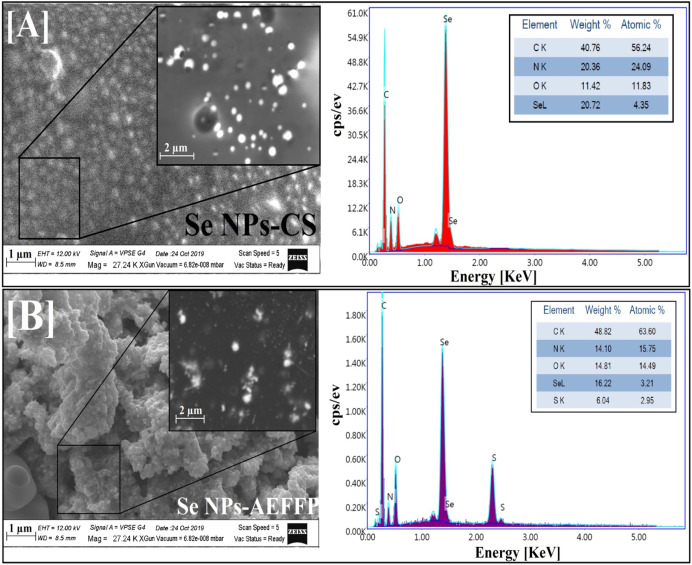
Factorial design-optimized and gamma irradiation-assisted fabrication of selenium nanoparticles by chitosan and Pleurotus ostreatus fermented fenugreek for a vigorous in vitro effect against carcinoma cells
The novelty of the present work looks in the synthesis of aqueous dispersed selenium nanoparticles (Se NPs) using gamma rays with the aid of various natural macromolecules such as citrus pectin (CP), sodium alginate (Alg), chitosan (CS) and aqueous extract of fermented fenugreek powder (AEFFP) using Pleurotus ostreatus for investigating their impact in vitro toward carcinoma cell. The synthesized Se NPs were characterized by XRD, UV–Vis., DLS, HRTEM, SEM, EDX and FTIR. Nucleation and growth mechanisms were also discussed. The factorial design was applied to examine the importance of multiple
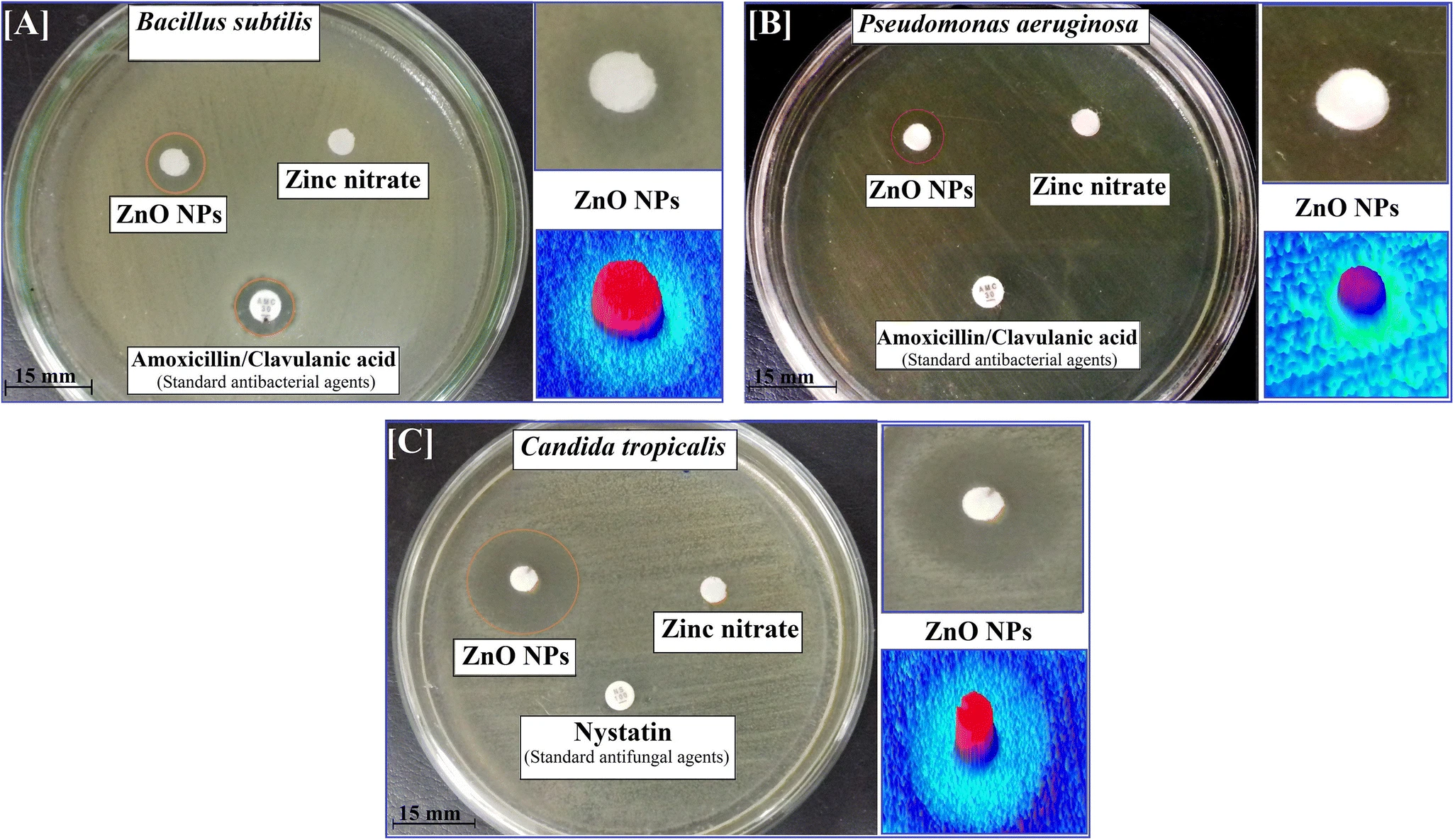
Fabrication of Ultra-Pure Anisotropic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Simple and Cost-Effective Route: Implications for UTI and EAC Medications
The purposes of this work are to evaluate the antimicrobial, antibiofilm, anticancer, and antioxidant abilities of anisotropic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) synthesized by a cost-effective and eco-friendly sol–gel method. The synthesized ZnO NPs were entirely characterized by UV-Vis, XRD, FTIR, HRTEM, zeta potential, SEM mapping, BET surface analyzer, and EDX elemental analysis. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of ZnO NPs were investigated against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria and yeast causing serious diseases like urinary tract infection (UTI). The anticancer activity was
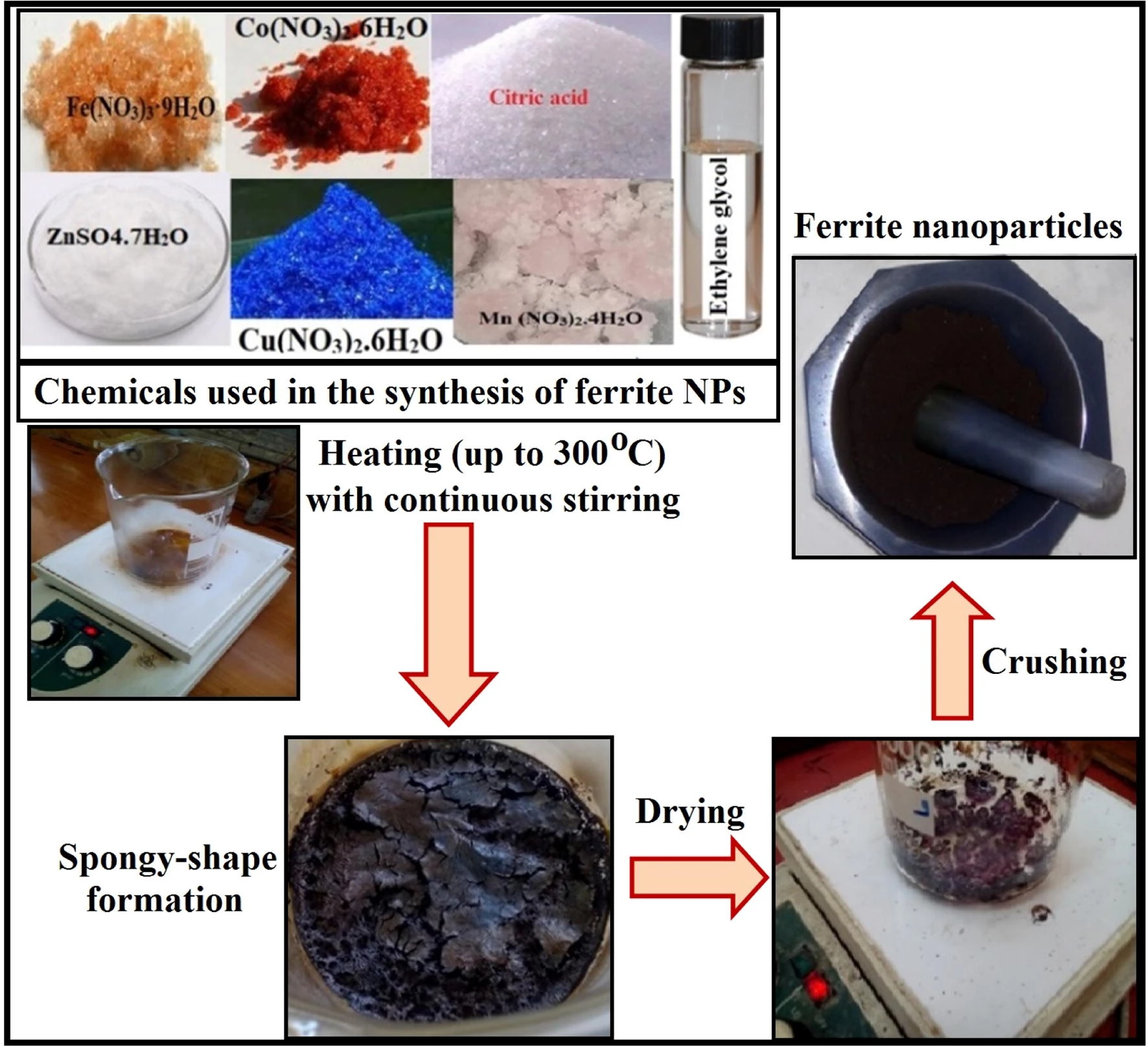

Controllable synthesis of Co1−x MxFe2O4 nanoparticles (M = Zn, Cu, and Mn; x = 0.0 and 0.5) by cost-effective sol–gel approach: analysis of structure, elastic, thermal, and magnetic properties
Substitutions of cations were considered to be the main way for improving the performance of ferrite nanocrystalline structures. In this paper, non-magnetic and magnetic ions were conducted to substitute cobalt spinel ferrite nanoparticles CoFe2O4 NPs (CFO NPs). The studied Co1−xMxFe2O4; M = Zn, Cu, and Mn; x = 0.00, and 0.50) samples were synthesized through a cost-effective sol–gel technique. The outstanding properties of the samples are addressed using XRD, FTIR, the inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES), Raman analyses, HR-TEM, BET surface area analyzer, the
The design of x-ray film reader with film presence detector
X-Ray viewer is a tool for observing the results of X-Ray films using ray lighting. It aims to get clearer readings of X-Ray films by radiographers and doctors. X-Ray viewers in hospitals generally cannot be carried anywhere because they use fluorescent lamps as a source of radiation and use 220 Volt AC voltage directly. So that its use is less effective and efficient because it must be connected directly to a 220 Volt AC power source and requires large power. In this regard the author wants to design an X-Ray viewer tool that can be used to read the results of X-Ray films clearly and is
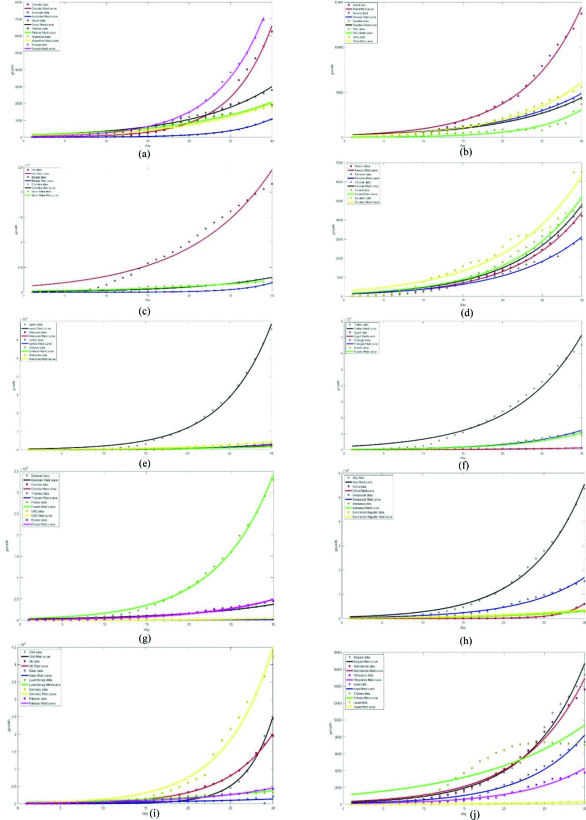
Modeling the effect of population density on controlling Covid-19 initial Spread with the use of MATLAB numerical methods and stringency index model
The effect of population density on the initial spread of the novel Covid-19 virus has been evaluated using the numerical data of fifty pioneer adopting countries in their first thirty days experience with the disease. The fifty countries were curdled into ten groups that each of them possesses an average population density and each group's virus's spread was modeled in a two-dimensional graph with the use of MATLAB curve fitting. The modeling is done based on the exponential growth equation. The stringency index model was also utilized a source of analysis regarding the government responses
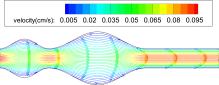
Numerical simulation of blood flow in abdominal aortic aneurysms: Effects of blood shear-thinning and viscoelastic properties
In this study numerical simulation of blood flow in abdominal aortic aneurysms is presented. The novelty in this study is the consideration of the blood viscoelastic properties to account for the presence of red blood cells in addition to the shear-thinning behavior. The Oldroyd-B model is used to account for the viscoelasticity while the Carreau–Yasuda model is used to represent the shear-thinning property. The artery with its aneurysms is modeled as a planar channel with rigid wavy walls. The governing equations are solved numerically using the Galerkin/least-squares finite element method
Modelling and Analysis the Population Density Effect on the Infectiousness Rate of COVID-19 Novel Virus and the Mortality Rate Percentage Regarding Oxford’s Stringency Index Model of Governmental Response in MATLAB
Numerical data on fifty pioneer adopting countries of Covid-19 novel pandemic has been put into study each on their first month of the virus’s spread. Ten groups were created with each including the countries of around the same average population density. This was meant to study the difference between each group’s growth of infected cases in addition to their mortality percentage rates (MPR). Modeling was done for each group with the use of MATLAB; for the growth rate, the exponential growth equation was considered, and for the mortality rate percentage, the equation was modeled over the span
Centralized Multi-agent Mobile Robots SLAM and Navigation for COVID-19 Field Hospitals
In this paper we focus on the proof of concept prototype of fully autonomous centralized Multi-Robot System (MRS) consisting of a Hexapod walking robot and a six wheeled mobile robot. Recently, there has been an increasing demand for such systems as they can be involved in several tasks such as collaborative search and rescue, surveillance, monitoring, and disinfecting Field hospitals. To name a few, COVID-19 pandemic showed the weak points in the medical sector around the world, including those in the most advanced nations that had to go through hard decisions due to the lack of medical
Comparative study of fractional filters for Alzheimer disease detection on MRI images
This paper presents a comparative study of four fractional order filters used for edge detection. The noise performance of these filters is analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) of the detected images is numerically compared. The mean square error (MSE) of the detected images as well as the execution time are also adopted as evaluation methods for comparison. The visual comparison of the filters capability in medical image edge detection is presented, that can help in the diagnosis of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
