Real-Time Dorsal Hand Recognition Based on Smartphone
The integration of biometric recognition with smartphones is necessary to increase security, especially in financial transactions such as online payments. Vein recognition of the dorsal hand is superior to other methods such as palm, finger, and wrist, as it has a wide area to be captured and does not have any wrinkles. Most current systems that depend on dorsal hand vein recognition do not work in real-time and have poor results. In this paper, a dorsal hand recognition system working in real-time is proposed to achieve good results with a high frame rate. A contactless device consists of a
Assessment of cardiac mass from tagged magnetic resonance images
Purpose: Tagged and cine magnetic resonance imaging (tMRI and cMRI) techniques are used for evaluating regional and global heart function, respectively. Measuring global function parameters directly from tMRI is challenging due to the obstruction of the anatomical structure by the tagging pattern. The purpose of this study was to develop a method for processing the tMRI images to improve the myocardium-blood contrast in order to estimate global function parameters from the processed images. Materials and methods: The developed method consists of two stages: (1) removing the tagging pattern

Native Mobile Applications UI Code Conversion
With the widespread use of mobile applications in daily life, it has become crucial for software companies to develop the applications for the most popular platforms like Android and iOS. Using a native development is time consuming and costly. Cross-platform mobile development like Xamarin and React native emerged as a solution to the mentioned problem of native development for the time and cost. Meanwhile it requires the developers to learn a new language. Other tools are converting the mobile apps of specific platform to the corresponding platform, but most of them still lack the mobile

Stock exchange threat modeling, EGX as a case study
Cyber crime is a growing threat affecting all business sectors. Stock Exchanges, a financial services sector, are not far from it. Trading stocks via Internet exposes the process to cyber threats that might take advantage of a system defect to breach security and cause possible harm. Online Trading websites are protected by various security systems. Digital Certificate, which is based on Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol, is an example. This research examines implementation of Digital Certificate in online trading servers. This evaluation helps to identify security weaknesses and take actions
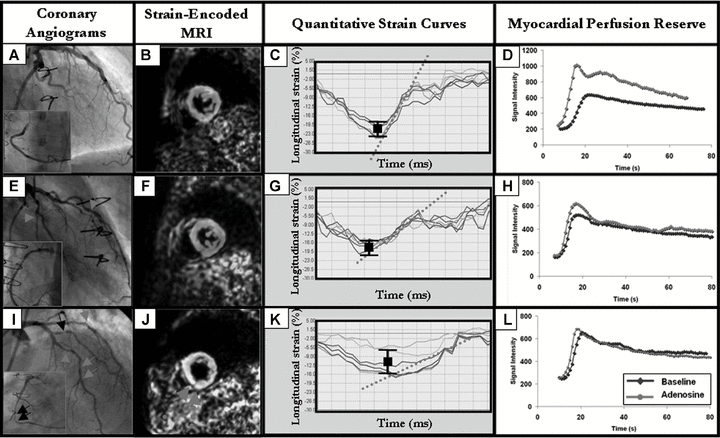
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance for the evaluation of chronic allograft vasculopathy in transplant recipients
The aim of our study was to investigate the ability of Strain-Encoded magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) in heart transplantation (HTx)-recipients. In consecutive subjects (n = 69), who underwent cardiac catheterization, MRI was performed for quantification of myocardial strain and perfusion reserve. Based on angiographic findings subjects were classified: group A including patients with normal vessels; group B, patients with stenosis
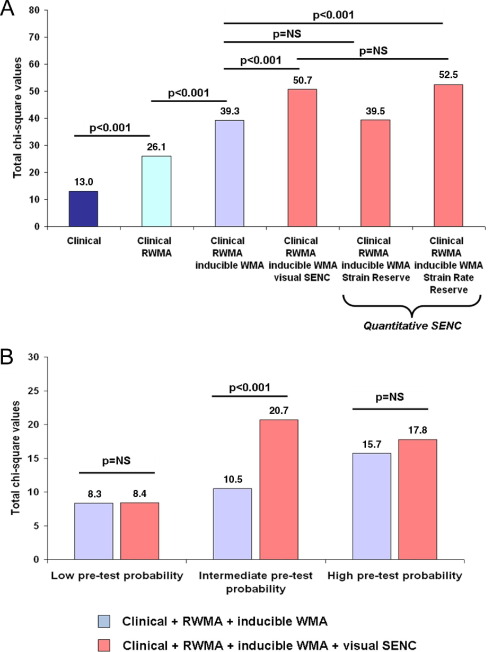
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance during high-dose dobutamine stress testing for the estimation of cardiac outcomes: Comparison to Clinical Parameters and Conventional Wall Motion Readings
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the prognostic value of strain-encoded magnetic resonance imaging (SENC) during high-dose dobutamine stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (DS-MRI) compared with conventional wall motion readings. Background: Detection of inducible ischemia by DS-MRI on the basis of assessing cine images is subjective and depends on the experience of the readers, which may influence not only the diagnostic classification but also the risk stratification of patients with ischemic heart disease. Methods: In all, 320 consecutive patients with suspected or

Multi-view human action recognition system employing 2DPCA
A novel algorithm for view-invariant human action recognition is presented. This approach is based on Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) applied directly on the Motion Energy Image (MEI) or the Motion History Image (MHI) in both the spatial domain and the transform domain. This method reduces the computational complexity by a factor of at least 66, achieving the highest recognition accuracy per camera, while maintaining minimum storage requirements, compared with the most recent reports in the field. Experimental results performed on the Weizmann action and the INIRIA IXMAS
In silico identification of potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer
Background: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide and is the most commonly diagnosed cancer. Like other cancers, it is a complex and highly heterogeneous disease involving multiple signaling pathways. Identifying potential therapeutic targets is critical for the development of effective treatment strategies. Methods: We used a systems biology approach to identify potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer. We first identified genes that were differentially expressed between smokers with normal lungs and those with cancerous lungs, then integrated
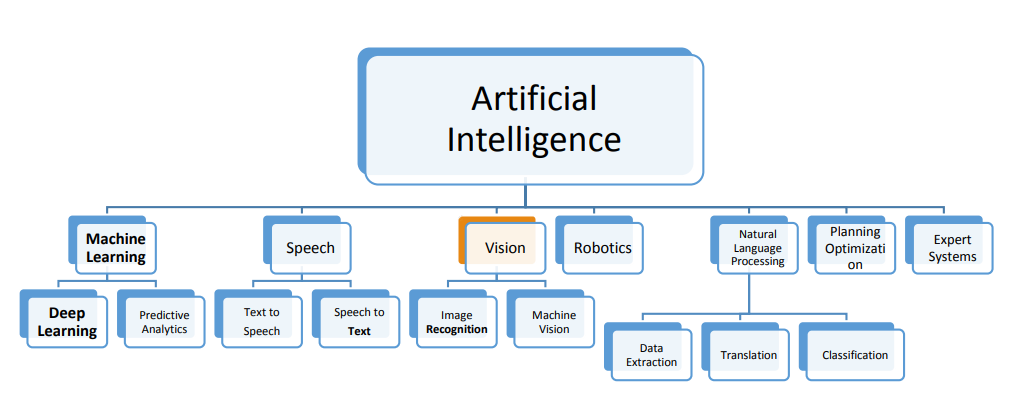
Artificial intelligence for retail industry in Egypt: Challenges and opportunities
In the era of digital transformation, a mass disruption in the global industries have been detected. Big data, the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are just examples of technologies that are holding such digital disruptive power. On the other hand, retailing is a high-intensity competition and disruptive industry driving the global economy and the second largest globally in employment after the agriculture. AI has large potential to contribute to global economic activity and the biggest sector gains would be in retail. AI is the engine that is poised to drive the
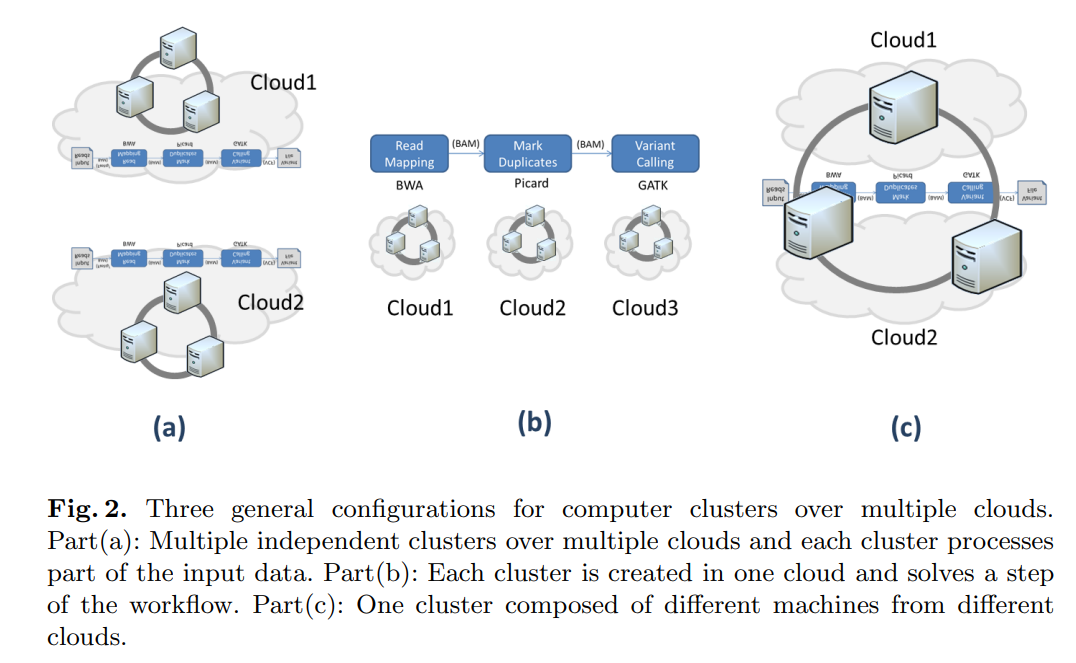
Supporting bioinformatics applications with hybrid multi-cloud services
Cloud computing provides a promising solution to the big data problem associated with next generation sequencing applications. The increasing number of cloud service providers, who compete in terms of performance and price, is a clear indication of a growing market with high demand. However, current cloud computing based applications in bioinformatics do not profit from this progress, because they are still limited to just one cloud service provider. In this paper, we present different use case scenarios using hybrid services and resources from multiple cloud providers for bioinformatics
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
